Delve into the intricate relationship between gut health and brain function as we uncover the fascinating interplay that shapes our overall well-being. Through this exploration, we aim to shed light on the crucial role of gut health in influencing cognitive processes and emotional balance.
As we navigate through the complexities of the gut-brain axis, a deeper understanding awaits, offering insights into how our dietary choices and lifestyle habits can profoundly impact our mental and emotional states.
Importance of Gut Health
Having a healthy gut is crucial for overall well-being as it plays a significant role in various bodily functions.
The Role of the Gut Microbiome
The gut microbiome, which consists of trillions of microorganisms, helps in digestion, nutrient absorption, and even influences the immune system.
Impact on the Immune System
- A healthy gut is essential for a strong immune system as about 70% of the body's immune cells are located in the gut.
- An imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to inflammation and weaken the immune response, making the body more susceptible to infections and diseases.
Effect on Nutrient Absorption
Proper gut health is vital for the absorption of nutrients from the food we eat. If the gut is not functioning optimally, it can lead to malabsorption issues and deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals.
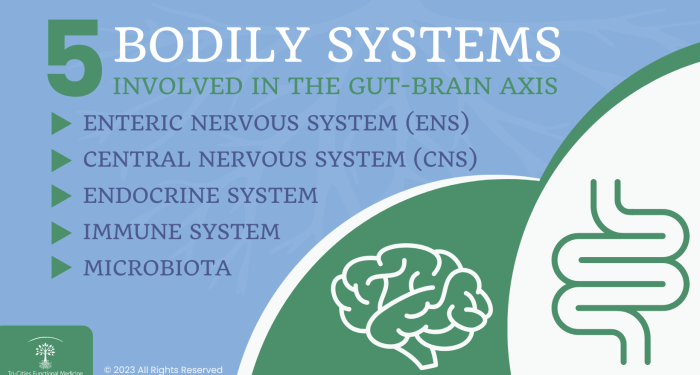
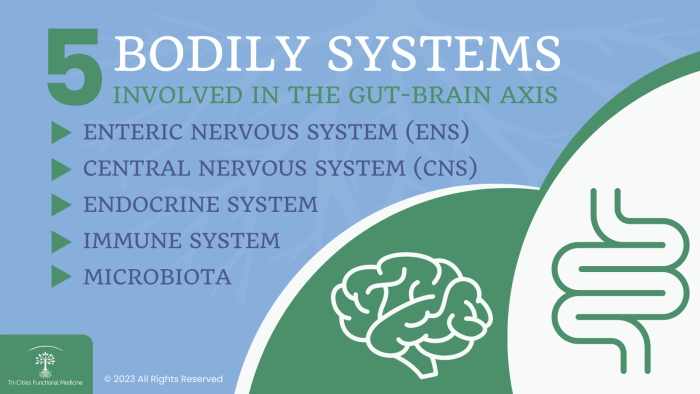
Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis refers to the bidirectional communication system between the gastrointestinal tract and the brain. This complex network involves neural, hormonal, and immunological signaling pathways that play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
How the Gut Communicates with the Brain
The gut communicates with the brain through several mechanisms, including the vagus nerve, the enteric nervous system, and the production of various neurotransmitters and hormones. The vagus nerve serves as a direct line of communication between the gut and the brain, transmitting signals that can influence mood, behavior, and cognitive function.
The enteric nervous system, often referred to as the "second brain," consists of a network of neurons within the gastrointestinal tract that can operate independently of the central nervous system. Additionally, gut bacteria produce neurotransmitters such as serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which can impact brain function and mental health.
Influence of Gut Bacteria on Brain Function
The gut microbiota, which consists of trillions of microorganisms residing in the gastrointestinal tract, plays a significant role in influencing brain function. These bacteria produce various metabolites and neurotransmitters that can cross the blood-brain barrier and affect neural activity. Imbalances in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, have been linked to conditions such as depression, anxiety, and neurodegenerative diseases.
By maintaining a healthy gut microbiome through proper diet, probiotics, and lifestyle choices, individuals can support optimal brain function and mental well-being.
Gut Health and Mental Health
When it comes to mental health, the connection to gut health is not often immediately apparent. However, research has shown that the health of our gut can significantly impact our mental well-being.
Impact on Mood and Behavior
Our gut is often referred to as our "second brain" due to the strong connection between the gut and the brain. The gut is home to millions of neurons that communicate with the brain through the gut-brain axis. When our gut health is compromised, it can lead to disruptions in this communication, affecting our mood and behavior.
- Imbalance in gut bacteria can lead to inflammation, which has been linked to symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- Studies have shown that individuals with certain gut bacteria imbalances are more likely to experience mood disorders.
- Disruptions in gut health can also impact the production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, which plays a crucial role in regulating mood.
Factors Affecting Gut Health
Various factors play a crucial role in determining the health of our gut. This includes dietary choices, stress levels, and even the medications we take.
Dietary Factors Impacting Gut Health
Our diet has a direct impact on the health of our gut. Certain foods can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut, while others can lead to imbalances in the microbiome.
- High-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help nourish the gut microbiota.
- Probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and sauerkraut can introduce beneficial bacteria into the gut.
- On the other hand, diets high in processed foods, sugar, and unhealthy fats can negatively impact gut health.
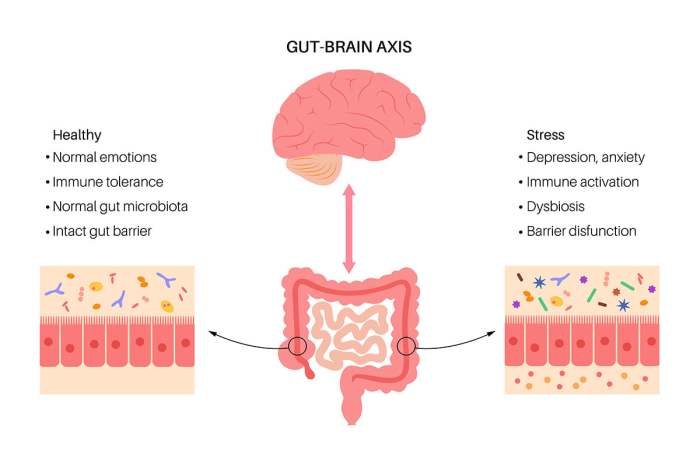
Role of Stress in Gut Health
Stress can significantly affect the health of our gut. The gut-brain axis, a bidirectional communication system between the brain and the gut, plays a key role in this relationship.
- Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and increase inflammation in the gut.
- Stress management techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, and exercise can help improve gut health.
Impact of Medications on the Gut Microbiome
Certain medications can alter the composition of the gut microbiome, affecting its diversity and function.
- Antibiotics, while necessary to treat infections, can also kill off beneficial bacteria in the gut.
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can damage the gut lining and disrupt the balance of gut bacteria.
- It is essential to discuss potential gut-related side effects of medications with a healthcare provider.
Strategies for Improving Gut Health
Improving gut health is essential for overall well-being as it plays a crucial role in various bodily functions, including immune response and nutrient absorption. Here are some strategies to enhance gut health:
Dietary Tips for Promoting a Healthy Gut
- Incorporate high-fiber foods such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes to support a diverse microbiome.
- Limit processed foods, sugar, and artificial sweeteners that can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria.
- Include fermented foods like yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi to introduce beneficial probiotics into your diet.
Importance of Probiotics and Prebiotics
- Probiotics are live beneficial bacteria that can help restore and maintain a healthy gut microbiota.
- Prebiotics are non-digestible fibers that serve as food for probiotics, promoting their growth and activity in the gut.
- Consuming a combination of probiotics and prebiotics can improve gut health and overall digestion.
Lifestyle Changes that can Support Gut Health
- Manage stress through relaxation techniques like meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, as stress can negatively impact gut health.
- Get regular physical activity to promote healthy digestion and maintain a balanced gut microbiome.
- Adequate sleep is essential for gut health, as it allows the body to repair and regenerate cells, including those in the gut lining.
Wrap-Up
In conclusion, the dynamic interconnection between gut health and brain function underscores the importance of nurturing our gut microbiome for optimal cognitive function and emotional well-being. By prioritizing gut health, we pave the way for a healthier mind and body, establishing a foundation for holistic wellness.
FAQs
Can gut health impact mood and behavior?
Yes, gut health plays a significant role in influencing mood and behavior due to the connection between the gut and brain.
What are some dietary tips for promoting a healthy gut?
Eating a diverse range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and fermented foods can promote a healthy gut.
How can stress affect gut health?
Chronic stress can disrupt the balance of gut bacteria and lead to digestive issues.
What role do probiotics and prebiotics play in gut health?
Probiotics introduce beneficial bacteria to the gut, while prebiotics serve as food for these bacteria, promoting a healthy gut microbiome.